Human data
In this guide
In this guideOn this page
Skip the menu of subheadings on this page.This is a discussion paper. It does not reflect the views of the Committee. It should not be cited.
Clinical data
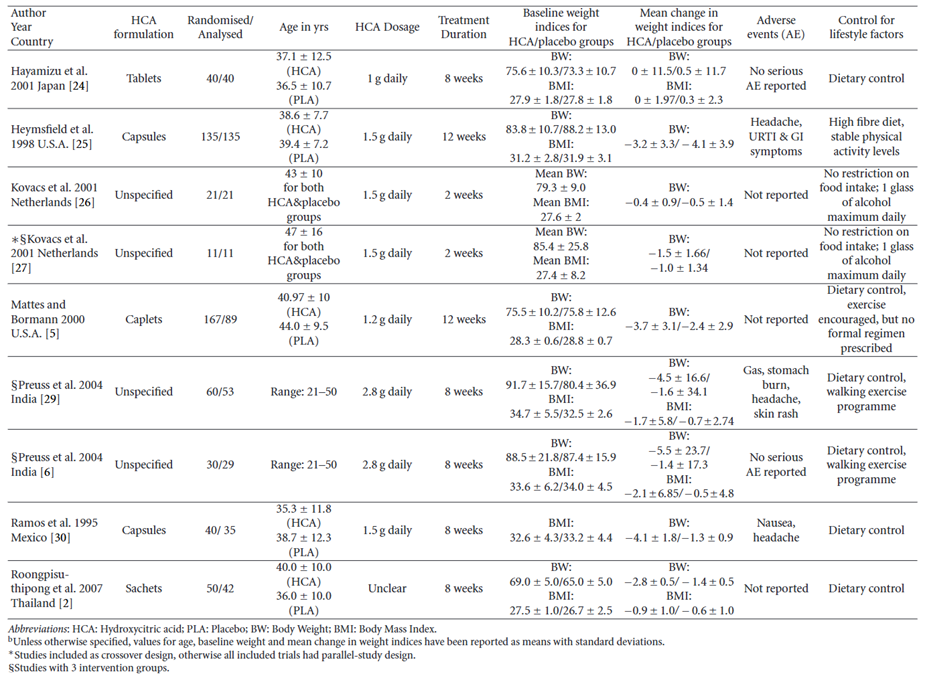
133. Onakpoya et al., (2010) performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of RCTs on the use of Garcinia extract (HCA) as a weight loss supplement. Twenty-three eligible trials were identified of which twelve were further analysed. Nine of the twelve trials provided data for statistical pooling (see Figure 4). The dosage of HCA and the duration of the study were varied, ranging from 1-2.8 grams daily and from 2 to 12 weeks, respectively. The adverse effects reported in the RCTs included headache, skin rash, common cold, and gastrointestinal symptoms. In most of the studies there were no “major” differences in adverse events between the HCA treatment and placebo groups. Except for one trial where gastrointestinal symptoms were twice as frequent in the HCA group compared to the placebo group (Heymsfield et al., 1998).
Figure 4 - Results table for studies with adequate data for meta-analysis (reproduced from Onakpoya et al., 2011).
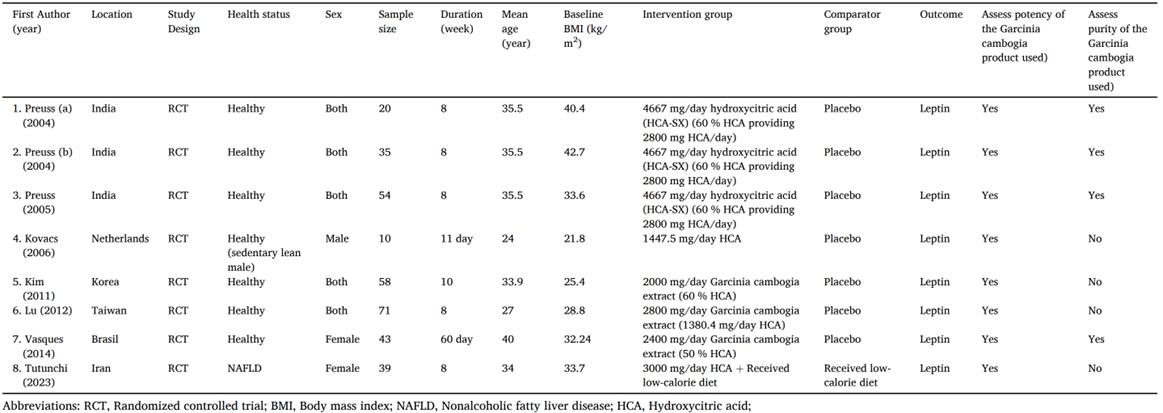
134. Amini et al., (2024) performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of RCTs on the use of G. cambogia (HCA) on serum leptin concentrations. Eight studies were included in the meta-analysis (see Figure 5). Leptin is a peptide hormone that is produced and secreted by adipose tissue. It plays a role in appetite control, immune system modulation, insulin sensitivity, blood pressure regulation and energy homeostasis. The authors observed that several of the included studies found no adverse effects of supplementation. In one study, 38.4% of participants reported the following side effects during treatment: gastrointestinal symptoms, thirst, dizziness and diuresis with gastric discomfort being the commonly reported (Vasques et al., 2014). It was noted by the authors that the treatment period in the selected trials ranged from 11 days to 10 weeks and the long-term side effects of supplementation requires further evaluation as several case reports observed liver injury following G. cambogia supplementation.
Figure 5 - Demographic characteristics of the included studies (reproduced from Amini et al., 2024).