Position paper on chitosan in bio-based food contact materials
On this page
Skip the menu of subheadings on this page.Background
1. The use of fossil-based plastics has been associated with adverse environmental impacts. Consequently, there is interest in reducing the amount of conventional plastic used for packaging, and recent years have seen a major global increase in the development and use of bio-based food contact materials (BBFCMs). Bio-based materials are defined as being derived, directly or indirectly, from a renewable source of living matter (Bradley, 2010).
2. Some BBFCMs under development contain chitosan, which is a biodegradable polysaccharide derived from chitin (Figure 1). Modifying chitosan by the addition of a metal has been shown to enhance its antimicrobial activity compared to native chitosan (Du et al., 2009). Consequently, some chitosan-based BBFCMs in development are nanoengineered to contain metal ions, such as copper (Yin et al., 2018).
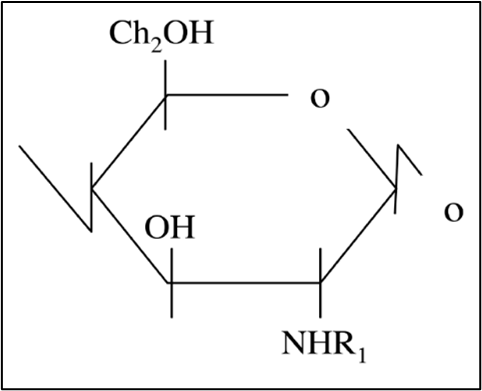
3. Chitin is a high molecular weight β(1,4)-linked homopolymer of N-acetylglucosamine (see Figure 1). In situ, chitin is linked to other structural components, such as protein and glucan, to form a protein-chitin matrix (Romano et al., 2007). Chitin is converted to chitosan by removing the acetyl groups (COCH3).
Figure 1: Chemical structures of chitin (R1 = COCH3) and chitosan (R1 = H).
4. Presently, the main commercial source of chitosan is from chitin obtained from waste streams of the fishing industry, i.e. crustacean shells. However, the recent increased global demand for chitosan has drawn attention to other possible sources: fungi and insects.
5. Production of chitosan from chitin involves deproteination and subsequently deacetylation. However, since the level of deproteination reported in studies from the literature is <100 % and any residual protein in chitosan might contain allergenic proteins (Yadav et al. 2019), there is a concern regarding the potential allergenicity of chitosan when used in Food Contact materials (FCM).
Life Cycle Assessments
6. Information on the Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of BBFCMs has been produced during their development. Regulatory guidance for conducting LCAs exists in various countries and regions, such as the European Union’s Product Environmental Footprint (PEF) guidelines and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) guidance in the United States. These regulatory documents provide standardised methodologies and data requirements for conducting LCAs that meet the needs of regulatory agencies and stakeholders. Similar initiatives are noted in other countries such as Canada, Japan, and China, which draw on international standards like those of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
7. The ISO guidelines, specifically ISO 14040:2006, provide a common framework for conducting LCAs. These guidelines outline four key processes of LCA: goal and scope definition, inventory analysis (quantifying inputs and outputs), impact assessment, and interpretation. Inputs include materials, energy, and water, while outputs encompass emissions, waste, and other environmental impacts.
8. SimaProTM is a popular life cycle assessment (LCA) tool developed by PRé Sustainability, used for evaluating the environmental impacts of products, processes, and services throughout their lifecycle. SimaProTM focuses on quantifying environmental impacts, including particulate matter (PM) emissions, but does not directly model the formation of particulates during product use or disposal phases, potentially requiring supplementary data.
9. Normalisation involves the aggregation and comparison of environmental impact categories to reference values. This allows for the expression of environmental impacts as ratios or percentages, aiding the comparison of different impacts within the same category, such as Global Warming Potential (GWP).
10. On the basis of such LCA, Ghosh & Katiyar (202) concluded that bio-based products have less impact on the environment in comparison to fossil-based products.
Shellfish allergy
11. According to Anaphylaxis UK (a charity supporting people living with serious allergies), there are different types of shellfish which can all cause allergic reactions. Shellfish can be split up into two groups, crustaceans and molluscs. Crustaceans include crab, lobster, crayfish and prawns. Molluscs can be split up further into bivalves (which include mussels, oysters, razor shells, scallops and clams), gastropods (which include limpets, periwinkles and snails found on land) and cephalopods (which include squid, octopus and cuttlefish).
12. Anaphylaxis UK state that “If you react to one type of shellfish it’s likely you’ll react to others in the same group. For example, if you react to crabs, it’s likely you’ll react to other crustaceans. You might react to shellfish in the other group as well, in this case molluscs”. This phenomenon is called cross-reactivity.
13. However, very few molluscan species contain chitin (in general, it is crustaceans that contain chitin). Therefore, allergies to shellfish would not be very relevant to a possible cross-over effect based only on the presence of chitosan. Rather, it is the protein contamination that could cause a problem for people with molluscs if they are allergic to crustaceans.
14. Anaphylaxis UK go on to explain that “An allergic reaction (including anaphylaxis) happens when the body’s immune system wrongly identifies a food or substance as a threat. When this happens, the body releases chemicals, such as histamine, in response. It is the release of these chemicals that causes symptoms”. Furthermore, “The symptoms of a shellfish allergy usually come on quickly, within minutes of eating the food. Mild to moderate symptoms may include: a red raised rash (known as hives or urticaria) anywhere on the body, a tingling or itchy feeling in the mouth, swelling of lips, face or eyes, and stomach pain or vomiting. The term for a more serious reaction is anaphylaxis. Most healthcare professionals consider an allergic reaction to be anaphylaxis when it involves difficulty breathing or affects the heart rhythm or blood pressure”. Anaphylaxis can be life-threatening.
15. In their review of shellfish allergy, Lopata et al. (2010) noted that cross-reactivity occurs frequently to seafoods within a certain group or family such as crab, lobster, shrimp among the crustaceans, suggesting that cross-reactivity frequently occurs between phylogenetically related organisms. Furthermore, crustacean allergic subjects often react to species of the mollusc group, such as squid (cuttlefish), abalone, limpet, squid, oyster, mussel, scallop and clam. Lopata et al. concluded that tropomyosin seems to be the major allergen responsible for molecular and clinical cross-reactivity between crustaceans and molluscs.
16. Although tropomyosin is the major allergen identified in crustaceans, several other allergenic proteins including arginine kinase and myosin light chain have been identified in shrimp and other crustacean shellfish as well as molluscan shellfish (EFSA, 2014). Tropomyosin is a muscle protein present in all species of vertebrates and invertebrates. However, only the tropomyosin found in invertebrates such as crustaceans, arachnids, insects, and molluscs has been associated with allergic reactions in humans (Reese et al., 1999).
17. Tropomyosin is a heat-stable allergen (Daul et al., 1994). It is also an “acidic” protein with an isoelectric point (pI) value of 4.5 (Reese et al., 1999). Due to these characteristics, tropomyosin can be present in processed foods (Reese et al., 1999). However, in their review of shellfish allergy, Woo & Bahna (2011) note that tropomyosin’s “allergenicity may change by certain processing methods. Boiling may result in the Maillard reaction (glycation) and formation of neoepitopes, as demonstrated that in some patients, boiled shrimp extract induced larger skin test responses than raw extract. Also, shrimp extract treated with high intensity ultrasound for 180 minutes demonstrated decreased binding with sera from shrimp allergic patients”.
18. In the PhD thesis of Nguyen (2012), results of a dot blot experiment demonstrated the presence of tropomyosin in technical samples of chitin and chitosan samples (these samples were provided by Mahidol University in Thailand). Furthermore, an inhibition enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) confirmed the immunoreaction of the protein residue in chitin and chitosan samples to rabbit sera (which was specific to shrimp tropomyosin). Subsequently, Nguyen (2012) noted that “special care should be taken when using chitin and chitosan in food or medical preparations. Warning statements should state clearly the presence of tropomyosin in products derived from chitin or chitosan, especially when the consumers are sensitised to crustaceans”.
Chitin & chitosan-based BBFCMs in development
19. Food packaging materials containing chitosan are being developed in the form of flexible films or coatings. A “film” is preformed separately and wrapped onto a food surface. These films are usually prepared by using a solvent casting method, in which chitosan is dissolved in suitable solvents (in most cases, slightly acidified water) and then poured onto a flat surface to allow the solvent to evaporate (Kim et al., 2006). On the other hand, a “coating” is a thin layer formed directly onto the surface of food and/or its packaging. Direct application of chitosan formulations onto food surfaces can be attained by spraying or dipping (Tharanathan, 2003). Additionally, drinking straws which contain chitosan have also been developed (see paragraph 44).
20. In studies found in the literature, chitosan-based films may be described as edible or inedible, whereas chitosan coatings are almost always described as edible since they form a layer directly on the top surface of the food (Priyadarshi & Rhim, 2020). Another difference is that chitosan films are >30 µm in thickness, whilst coatings are <30 µm in thickness (Van den Broek et al., 2015). However, with the advancement of nanotechnology, nano-coatings are being explored, which consist of nanoscale layers (<100 nm) built-up onto food surfaces (Vasile, 2018). In their review of nanoedible films for food packaging, Jeevahan & Chandrasekaran (2019) noted that production of edible films and coatings was still largely at the laboratory level and was not yet expanded to industrial level due to their high cost of production.
21. It has been suggested that chitosan-based films could appear in vacuum-packaged processed meat (Ouattara et al., 2000), cheese (Fajardo et al., 2010), and other foods such as vegetables, fruits, grains, and fish (Sinha et al., 2012).
22. Some BBFCMs in development contain chitin, in the form of nanofibers (Ifuku & Saimoto, 2012) or nano-whiskers (Zeng et al., 2012). Incorporation of chitin nano-whiskers into starch-based films has been shown to improve the film’s mechanical and barrier properties (Qin et al., 2016). For chitin nano-whiskers migration studies are scarce, mainly due to the difficulties in characterising nanoparticles in composites generally, and the lack of methods for qualitative and quantitative analysis (Han et al., 2011).
Market uses of chitosan
23. Chitosan has applications in tissue engineering and biomedicine due to its low cost, biocompatibility, lack of toxicity, and biodegradability (Madhumathi et al., 2009; Konovalova et al., 2017).
24. Chitosan is widely used as a food additive and functional ingredient in foods sold in Italy, Finland, Korea and Japan (Peter, 1997; Singla & Chawla, 2001). Both chitin and chitosan are approved food additives in Japan (JFCRF, 2011). Furthermore, chitosan is listed as a processing aid in the Codex General Standard for Fruit Juices and Nectars (Codex, 2005). The Norwegian company “Norwegian Chitosan AS” trades chitosan (Kitoflokk™ and Norlife) for several applications, including food and beverages (Ferreira et al. 2016).
25. Chitosan and chitin have not been officially classified for GRAS (generally recognised as safe) status by the US Food and Drug Administration (US FDA) but some biotechnology companies have notified the US FDA of their view that the use of chitosan and chitin in specific food applications would be GRAS. For example, KitoZyme views the use of chitosan (derived from Aspergillus niger) in alcoholic beverage production (with chitosan being removed from the beverages post-treatment, using physical separation processes) as GRAS. In their correspondence to KitoZyme, the US FDA (2011) wrote: “based on the information provided by KitoZyme, as well as other information available to FDA, the agency has no questions at this time regarding KitoZyme’s conclusion that chitosan from A. niger is GRAS under the intended conditions of use. The agency has not, however, made its own determination regarding the GRAS status of the subject use of chitosan”.
26. Shellfish-derived chitosan is sold online as a dietary supplement, with manufacturer-recommended daily consumption of chitosan, for example, of 2.4 g and 3 g. It has been suggested that chitosan may support weight loss and lower cholesterol by eliminating fat and cholesterol from the body instead of allowing the body to absorb them (Moraru et al. 2018).
27. Chitosan is considered to be hemostatic due to its cationic nature (NTP, 2017), which supports its use in wound dressings. Wound dressings manufactured from shellfish-derived chitosan were introduced in 2005 for US soldiers, and in 2008 the US FDA approved the chitosan-based HemCon bandage for use as a dressing for local management of bleeding wounds (US FDA, 2008).
Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME)
28. Results from Chae et al. (2005) indicated that absorption of chitosan from the gastrointestinal (GI) tract following oral exposure in rats was inversely related to its molecular weight: oral gavage administration of chitosan with molecular weights of 3.8, 7.5, 13, 22, or 230 kDa resulted in maximum plasma concentrations of 20, 9, 6, 4, or <0.5 μg chitosan/mL, respectively.
29. Several chitinases have been identified in humans which can bind and degrade chitin (Boot et al., 2001). Furthermore, Lactococcus lactis and Lactobacillus plantarum have chitinolytic and/or chitin-binding proteins (Sánchez et al., 2011). These bacteria are an integral part of normal gut flora, fermented foods, and probiotic-fortified foods (Kim et al., 2013; Todorov et al., 2012).
30. Degradation of chitosan in vertebrates is thought to occur predominantly by lysozymes and bacterial enzymes in the colon (Kean & Thanou, 2010).
31. The depolymerised products of chitin or chitosan are called chitooligosaccharides (COS), which have a molecular weight of approximately 3.9 kDa or less (Lodhi et al., 2014). COS are water-soluble (Qin et al., 2006), and are reported to have antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial effects (Huang et al., 2016). However, COS have been observed to irritate intestinal epithelial mucosal tissues, stimulating them to produce mucin (Deters et al., 2008). Following depolymerisation, both chitin and chitosan particles are readily phagocytosed (Bueter et al., 2011).
Allergen reference doses
32. The major allergen identified in crustaceans is tropomyosin. However, no threshold levels for tropomyosin alone could be identified in the literature. However, studies conducted by Remington et al. (2020) and Houben et al. (2020) determined allergen eliciting doses for crustacean-derived protein, i.e. an ED01 (where <1 % of the allergic population may be expected to react) of 25 mg (95 % confidence interval of 2.7-166 mg) for shrimp protein, and an ED05 of 280 mg (95 % confidence interval of 69.3-880 mg). The ED01 and ED05 were derived from human food challenge data using dose-distribution modelling and represent acute intake levels of crustacean-derived protein that are predicted to provoke any objective reaction in no more than 1 and 5 % (respectively) of at-risk individuals, who show a minimal allergic response upon challenge. However, the severity of these reactions is variable. The large confidence intervals for both EDs reflect the uncertainties around those estimates for this allergenic food.
33. In 2023, an Expert Committee of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO) published a meeting report on the risk assessment of food allergens, which included consideration of threshold levels in foods for eight priority allergens (FAO/WHO, 2023). The Expert Committee recommended that reference doses (RfDs) should be based on ED05 values (FAO/WHO, 2023). The shrimp ED05 value of 280 mg shrimp protein was rounded down to a single significant figure on the basis of the size of the confidence interval. Thus, the Expert Committee recommended a RfD for crustacea of 200 mg crustacea (shrimp) protein because the analysis relied on a few species of shrimp to provide data for the group of crustacea and the additional, more conservative rounding was considered appropriate when considering the diversity of crustacea species consumed (FAO/WHO, 2023).
34. A subgroup of the Committee on Toxicity of Chemicals in Food, Consumer Products and the Environment (COT) assessed the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee’s report to inform the UK Food Standards Agency (FSA) and Food Standards Scotland (FSS) risk managers’ understanding of whether it is appropriate for the recommended reference doses based on ED05 values to be applied to the UK 14 regulated allergens, including crustaceans (TOX/2023/35). In addressing the questions posed in the Terms of Reference, the COT subgroup reached the following conclusions:
a) The COT subgroup were of the view that there is no reason to suppose the data on which the Codex Expert Committee based their analysis are not sufficiently representative of the UK population.
b) Key gaps identified by the COT subgroup that need to be addressed before the UK can adopt the recommended RfDs included some uncertainties regarding the way in which the ED values have been derived. However, the key gaps identified could not be filled using the published literature.
c) There is insufficient evidence to demonstrate that using RfDs based on ED05 rather than of ED01 values would not significantly impact on public health, and the choice of which allergen reference dose to use (ED05 or ED01) would be based on additional considerations, such as analytical feasibility.
35. The COT subgroup’s draft report was discussed by the full Committee at the July 2023 COT meeting. Members agreed with the COT subgroup’s methodology of assessment and the contents of the draft report, including the conclusions. Work by the FSA/FSS to determine appropriate allergen thresholds is still ongoing.
36. In EFSA’s 2014 evaluation of allergenic foods and food ingredients for labelling purposes, EFSA noted that “studies reporting on the prevalence of allergy to crustaceans in the general (unselected) European population are scarce. In the few studies available, the prevalence of self-reported crustacean-related adverse reactions to food in children ranged from 0.1 % and 0.3 % in Greece (Zannikos et al., 2008) and the UK (Pereira et al., 2005) to 5.5 % in France (Touraine et al., 2002). Figures reported from the Netherlands (Brugman et al., 1998), Sweden and Iceland (Kristjansson et al., 1999) were within that range (0.7–1.5 %). Prevalence of self-reported allergy to shrimp was 0.5 % in 2- to 14-year-old Finch [sic] children (Rancé et al., 2005). In adults, estimated sensitisation rates to crab in Germany (Schafer et al., 2001) based on positive skin prick tests (SPT) were similar to those reported in Hungary (Bakos et al., 2006) based on specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) testing (1.9 % and 1.8 %, respectively). Prevalence rates of allergy to crustaceans based on clinical history and positive SPT in the German general population were much lower (0.2 %) (Zuberbier et al., 2004). Only one study conducted in Denmark reported challenge proven prevalence data for shrimp allergy, which ranged from zero in subjects < 22 years to 0.3 % in subjects > 22 years (Osterballe et al., 2005)”.
37. Pereira et al. (2005) investigated the rates of food hypersensitivity (FHS) in UK teenagers against a panel of allergens including shellfish. These teenagers (11 and 15 year-olds) were resident on the Isle of Wight at the time of the study, and completed a questionnaire with their parents on adverse reactions to foods. Results showed that two 11 year-olds (0.3 %; n = 699), and five 15 year-olds (0.8 %; n = 649) reported an adverse event from consumption of shellfish.
38. From an analysis of UK hospital admission data from 1998 to 2018, Conrado et al. (2021) concluded that "hospital admissions for food induced anaphylaxis have increased from 1998 to 2018, however the case fatality rate has decreased”. From 1998 to 2018, in children (<16 years old) fish & crustacea triggered 6 % of all cases of fatal food induced anaphylaxis, whereas for adults it was 7 %.
Case reports of reactions to chitosan
39. Kato et al. (2005) reported a case of immediate-type allergy from use of a health food containing chitosan, where “the patient was a 47-year-old female person who developed systemic urticaria and difficulty in breathing after oral ingestion of chitosan. Since skin tests (prick test and scratch patch test) were positive, the test was done using another commercial chitosan, and was positive. The patient was diagnosed as having chitosan-induced immediately-type allergy, and was instructed to avoid ingestion of chitosan. The patient developed no symptoms thereafter”. The study authors concluded that chitosan may have functioned as a food allergen because of its molecular weight and general properties.
40. Two case reports were identified relating to hypersensitivity to some healthcare products containing chitosan (Cleenewerck et al., 1994; Pereira et al., 1998). The biological source of the chitosan was not stated in these publications.
Reactions from entomophagy
41. Reports on adverse reactions from insect consumption (entomophagy) are scarce and only two population studies (described below) were identified in the literature that reported on the prevalence of food allergy to insects. In these two studies, allergy did not seem to have been verified by clinical measurements, which was a limitation of the data.
42. Taylor & Wang (2018) investigated the prevalence of allergic reactions caused by consuming edible insects. The investigation was conducted in the North Eastern (or the Isan region) of Thailand, in an area where entomophagy is common. Information concerning entomophagy and allergic reactions was gathered from multiple sources in four locations: Nongki, Nang Rong, Nong Bun Mak, and Nakhon Ratchasima. The survey included questions about eating habits in relation to insects, other known food allergies, and presented a list of symptoms the participants may have experienced. The prevalence of allergic reactions caused by consuming edible insects was much higher than expected across the 2,500 respondents. In the Isan region, approximately 14.7 % of people experienced a single symptom indicative of an edible-insect allergy, and 7.4 % of people experienced multiple symptoms indicative of an edible-insect allergy. Furthermore, approximately 46.2 % of people that already suffered from a known food-based allergy also experienced symptoms indicative of an allergic reaction after insect consumption. According to the study authors, “the most common symptoms appear to be gastrointestinal (diarrhoea and vomiting)”. The study authors concluded that “the allergy aspect of entomophagy is a serious issue and has the potential to adversely affect the future of entomophagy, especially in introducing the concept to western cultures”.
43. Barennes et al. (2015) assessed the prevalence of food allergy to insects amongst insect-eaters. In this survey, eight teams (which included medical physicians) collected data to address socioeconomic characteristics of the consumers, types of insects consumed, frequency of consumption and reports of side effects. This study was conducted in Laos, and included 1,059 subjects that had previously eaten insects, 81 of whom (7.6 %) reported “allergy problems after eating insects”. Of these 81 subjects, 38 reported that allergy problems were “mostly with grasshoppers or stink bugs”. None of the subjects reported severe anaphylaxis. In this survey, it was not possible to identify how much the consumption of edible insects contributed to the daily diet of the population or provide detail on the way insects were harvested. The survey did not mention whether any clinical confirmation of the allergenic symptoms was undertaken.
UK incidents
44. The FSA has received a number of queries about the presence of chitosan in food packaging materials and chitosan-based drinking straws, but no incidents have formally been raised within the FSA. However, there was one report of a potential allergic reaction to the use of a chitosan-based straw in a pub which was reported to a local authority. The local authority carried out an investigation with the supplier of the chitosan-based straws but it was difficult to rule out cross-contamination from the meal that the individual had also consumed on the premises. The individual who suffered the allergic reaction did have a seafood allergy but did not disclose this to the pub. That was the only incident reported to the FSA but uncertainties remain over the cause of the allergic reaction.
UK legislative position
45. In retained European legislation, all materials and articles intended for contact with food must meet the requirements of the Framework Regulation (EC) No. 1935/2004. The principle underlying this Regulation is detailed in Article 3 which states: “materials and articles, including active and intelligent materials and articles, shall be manufactured in compliance with good manufacturing practice so that, under normal or foreseeable conditions of use, they do not transfer their constituents to food in quantities which could: a) endanger human health; b) bring about an unacceptable change in the composition of the food; c) bring about a deterioration in the organoleptic characteristics thereof.”
46. With regards to necessary labelling (and potential exposure to allergens) Article 15 of retained Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 states that ‘special instructions (are) to be observed for safe and appropriate use’. This labelling information may need to be provided on the packaging, or as a standalone warning should the item be sold loosely. If the item is marketed as edible, other labelling requirements come into play to comply with food law and the Materials and Articles in Contact with Food Regulations 2012 as amended.
47. Whilst there are no specific migration limits for BBFCMs, industry can refer to legislation that may be pertinent (the same holds true for other materials lacking specific legislation). Retained Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 states that: “According to good manufacturing practice it is feasible to manufacture plastic materials in such a way that they are not releasing more than 10 mg of substances per 1 dm2 of surface area of the plastic material”. Therefore, the Plastics Regulation stipulates a generic migration limit (maximum allowable) of 10 mg per square decimetre of surface area of material (10 mg/dm2). According to Retained Regulation (EU) No 10/2011, “The overall migration limit of 10 mg per 1 dm2 results for a cubic packaging containing 1kg of food to a migration of 60 mg per kg food. For small packaging where the surface to volume ratio is higher the resulting migration into food is higher”. The applicability of FCM legislation depends on the BBFCM’s intended use and how it is marketed. If the BBFCM is intended purely for containment purposes and is inedible, it is not food and comes under FCM legislation.
48. The EU considers that an edible film is a special active part of the food and, seen from a legal point of view, it is to be regarded as a foodstuff, along with the food packed in the film, having to fulfil the general requirements for food (Fabec et al., 2000); this is also the position of the FSA FCM Policy team. Consequently, the presence of a known allergen in an edible film or coating on a food must be clearly stated on the label (Campos et al., 2011). Due to hygene reasons, it is anticipated that food products in edible films need to have an outer package, otherwise the film should not be eaten (Fabec et al., 2000).
Evaluations of crustacean chitosan
2011 Evaluation by EFSA (EFSA NDA Panel)
49. In 2011, when reviewing a proposed health claim for a food supplement containing crustacean-derived chitosan, the EFSA Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA) Panel concluded, that “a cause and effect relationship has been established between the consumption of chitosan and maintenance of normal blood LDL-cholesterol concentrations”, and “considers that in order to obtain this effect in adults, 3 g of chitosan should be consumed daily” (EFSA, 2011). The Panel stated that their opinion does not constitute, and cannot be construed as, a positive assessment of its safety.
Studies from the literature
50. Studies designed to evaluate the effectiveness of shellfish-derived chitosan as an oral weight-loss supplement over 12 days suggest that it is well tolerated in men and women at 4.5 g chitosan per day (Gades & Stern 2003, 2005). However, these studies excluded subjects with food allergies and sensitivities. Data collection sheets for the volunteers did not appear to have a space for recording any adverse effects, but one of the 15 male participants reported “vomiting after a meal during the supplement period” (Gades & Stern 2003). Additionally, in a study involving 65 men and women, consumption of chitosan tablets (6.75 g of chitosan daily for eight weeks), was “found to be safe”, though common transient GI symptoms were reported (loose faeces, constipation, abdominal pain, repeated flatulence, abdominal bloating, and abdominal rumbling) (Tapola et al., 2008). However, the study excluded subjects with a history of severe allergic reactions (anaphylactic reaction) when exposed to fish or crustaceans.
51. In 2011, Waibel et al. (2011) investigated the safety of chitosan-based “HemCon®” bandages in patients who reported a shellfish allergy. Initial assessment included a detailed history, IgE SPT, and serum testing to shellfish allergens. Participants who demonstrated specific shellfish IgE underwent a bandage challenge. It was reported that of the 19 participants who were enrolled, ten completed the study as they had met the inclusion criteria. Seven (70 %) were male and the average age was 44.8 + [sic] 10 years. Nine (90 %) reported a shrimp allergy history and five (50 %) reported multiple shellfish allergies. All participants completing the study had positive SPT and serum IgE testing to at least one shellfish; eight (80 %) had shrimp positive SPT and ten (100 %) demonstrated shrimp-specific IgE. No participant had a positive SPT to chitosan powder or experienced an adverse reaction during bandage challenges. No protein bands were visualised during gel electrophoresis analysis of chitosan powder. The study authors concluded that all participants tolerated the HemCon bandage without reaction.
Evaluations of fungal chitin
2010 Evaluation by EFSA (EFSA NDA Panel)
52. In 2010, the EFSA panel on NDA assessed the safety of chitin-glucan as a novel food ingredient (EFSA, 2010). This chitin-glucan was derived from A. niger through a fermentation process, and therefore did not contain shellfish protein. The product (KiOnutrime-CG™) assessed by EFSA was composed of >90 % chitin-glucan (a structure that combines chitin and beta (1,3) glucan) and ≤ 6 % protein and was intended to provide a daily intake of 2 - 5 grams of chitin-glucan. The Panel reviewed a report showing no observed adverse effects at the highest dose administered (about 6.6 g/kg bw) in a 13-week rat study (TNO, 2009). Because this dose is approximately 80-fold higher than the maximum intended level of intake for humans on a g/kg bw basis, the Panel concluded that KiOnutrime-CG™ was safe as a food ingredient at the proposed conditions of use and at the proposed intake levels. The Panel assessed the risk of allergenicity on the basis of some allergenic enzymes that are synthesised by A. niger such as beta-xylosidase. The Panel concluded that “an allergenic risk cannot be ruled out but is expected not to be higher than from the consumption of other A. niger derived products”. The Panel also noted that since A. niger is commonly detected in various foods such as fruits and vegetables, it is therefore expected to occur in the diet of most individuals.
2012 Evaluation by FSANZ
53. In 2012, Food Standards Australia New Zealand (FSANZ) approved an application for the use of A. niger-derived chitosan as a processing aid for production of some beverages. In their risk assessment, FSANZ noted that
animal toxicity studies on chitosan preparations of various molecular weights and degrees of acetylation did not show any treatment-related adverse effects following oral administration at high doses. Furthermore, “a published review of human data from 13 clinical trials of up to six months duration found no adverse effects associated with oral chitosan (average daily dose 3.5 g) as a weight loss supplement. In view of the absence of adverse effects at high chitosan doses, a group acceptable daily intake (ADI) “not specified” was established for chitosan derived from fungi. Information was provided indicating negligible levels of fungal chitosan in wine following processing. Negligible levels would also be expected in beer and cider, while no residual fungal chitosan would be expected in alcoholic products derived from distillation”. The overall conclusion was that the “use of fungal chitosan as a processing aid for the production of wine, beer, cider, spirits and food grade ethanol is technologically justified and raises no public health and safety issues for consumers” (FSANZ, 2012).
Studies from the literature
54. Seaton & Wales (1994) conducted an 8-year follow-up study on clinical reactions to A. niger in a biotechnology plant producing citric acid by fermentation of molasses with A. niger. The authors concluded that A. niger was a weak antigen, and that simple hygiene measures were needed to protect the workforce.
Evaluations of insect chitin
2020 Evaluation by EFSA (EFSA NDA Panel)
55. In 2020, the EFSA NDA Panel published their opinion on the safety of dried yellow mealworm (Tenebrio molitor larva) as a novel food (NF) (EFSA, 2020). This evaluation was on the whole mealworm preparation (not just the insect chitin), and therefore was a more holistic assessment of a potential allergic response. The reported average chitin content of the NF in powder form was 6.42 ± 0.28 g/100 g across five batches (the NF was not reported to contain chitosan).
56. The NDA Panel noted that “yellow mealworms are consumed as part of the customary diet or for medicinal purposes in some non-EU countries worldwide. Their consumption by humans has been reported in Thailand (Hanboonsong et al., 2013), China (Feng et al., 2018) and Mexico (Ramos-Elorduy, 1997, 2009; Ramos-Elorduy and Moreno, 2004). Yellow mealworms are among the insect species permitted to be consumed as food in Korea by the Korean Food and Drug Administration (KFDA) (Kim et al., 2017). Additionally, in Australia and New Zealand yellow mealworms are considered as non-traditional, not novel foodstuff (FSANZ, 2020). Since 1 May 2017, T. molitor larva is among the insect species that can be legally introduced in the Swiss market as food (whole, chopped or ground)” (EFSA, 2020). Because of this history of use, and the absence of adverse effects described in the literature, the Panel concluded that “the NF is safe under the proposed uses and use levels”. The proposed use was as an ingredient in several food products, such as pasta-based dishes, and biscuits, for all population groups.
57. The NDA Panel also discussed the work of Broekman et al. (2017) which demonstrated the possibility of de novo human sensitisation to allergens in mealworm, which can result in food allergy. Broekman et al. (2015) demonstrated that thermal processing did not lower the allergic potential of mealworm allergens (EFSA, 2020). The Panel also noted that “the applicant provided the study of Velasquez (2015) who investigated the allergenic potential of yellow mealworm larvae using extracts of the NF and concluded that subjects allergic to arthropods and more specifically to crustaceans, should not consume the NF due to the risk of cross-reactivity”. Subsequently, the NDA Panel considered that “the consumption of the NF may induce primary sensitisation and allergic reactions to yellow mealworm proteins and may cause allergic reactions in subjects with allergy to crustaceans and dust mites. Additionally, allergens from the feed may end up in the NF”. Furthermore, the Panel recommended that research should be undertaken on the allergenicity of yellow mealworm, including cross-reactivity to other allergens.
Studies from the literature
58. Broekman et al. (2016) included 15 patients with shrimp allergy (based on specialist opinion and diagnostic testing) in a double-blind, placebo-controlled food challenge (DBPCFC) trial, and found that 13 of these patients also had mealworm allergy. The study authors noted that “when comparing the mealworm challenge outcome of 4 patients who also had a shrimp challenge, eliciting doses (ED5 and ED10) as well as severity were in the same range”, which “indicate(s) that mealworm is at least as allergenic as shrimp”, though “more mealworm challenge data are needed to confirm this initial analysis”. Subsequently, Garino et al. (2020) used the data from Broekman et al. (2016) to predict values for the ED05, ED10, and ED20, indicating where 5 %, 10 % and 20 % of the shrimp allergic population are predicted to react to mealworm proteins. The values for the ED05 were all 63, 128, and 147 mg of T. molitor protein, estimated using the Weibull, log-logistic, and log-probit distribution models, respectively.
FSA activity with respect to the development of BBFCMs containing chitosan
59. In addition to seeking the advice of the COT, the FSA is corresponding with a biotechnology company which is developing food packaging materials comprised of chitosan, as this provides a useful addition to the current state of knowledge for these materials.
COT consideration
60. The COT considered that additional information was needed in order to assess the risk of allergenicity of chitin- or chitosan-based BBFCMs. More information would be needed, in particular on the effects of processing but also additional data characterising the protein content in chitosan and the final BBFCMs (against chemical and enzymatic methods of deproteination), data on migration from, and consumption of, BBFCMs. Information on the total amount of residual protein (expressed as mg/g BBFCM) would be helpful for estimating health risks.
61. In order to assess the health risk from the use of BBFCMs containing chitosan, additional information would be needed, notably on the level of any allergenic proteins migrating from these packaging materials into food. Although chitosan has been incorporated into the composition of some BBFCM products, it was not clear whether the manufacturing processes of these BBFCMs further reduced the protein content within the chitosan and/or the allergenicity of these proteins. Therefore, it would be helpful to obtain protein migration data from BBFCM products that contain chitosan under expected conditions of use, alongside estimates of consumer use/consumption of these products in order to provide an estimation of consumer exposure to any allergenic proteins.
62. The COT noted that available clinical ingestion data (Gades & Stern 2003, 2005; Tapola et al., 2008) indicated that the immunological properties of chitin and chitosan were of low concern in the context of BBCFMs. Chitin was well tolerated in supplements at higher exposures than would be expected from the use of BBFCMs. However, some adverse effects were associated with high intakes of the raw materials in clinical studies, which were typically mild symptoms of gastrointestinal tract distress such as diarrhoea, bloating, or vomiting. The indications were however, that this was a relatively non-specific inflammatory reaction. The COT agreed that these adverse effects were not of concern for BBFCMs as the processing was likely to produce a more inert final material. Furthermore, the phagocytosis of small fragments of chitin or chitosan appeared to be the same as that of similar-sized particles in general.
63. The COT agreed that the limited information provided in a case report of immediate-type allergy for chitosan-containing health food (Kato et al., 2005) did not suggest any additional concerns. The COT noted that this reported case of immediate-type allergy was most likely due to residual protein from the shellfish source from which the chitosan supplement was derived. The COT agreed that the type of hypersensitivity described in the two case reports of hypersensitivity to some healthcare products containing chitosan (Cleenewerck et al., 1994; Pereira et al., 1998) very rarely, if ever, occurs in the context of food ingestion.
64. A submission by Primex to the US FDA in 2012 (GRAS Notice No. 443) contained a dossier including some approaches to protein measurement and analytical data for the ED01 and corresponding analysis. The COT noted that the chitosan used in this submission appeared to be highly controlled in terms of its production, and whilst its specification may be unlike that of other chitosan products, it nevertheless provided a standard to be achieved and possibly put forward. The Committee agreed that during manufacture of BBFCMs, the chitosan used needed to have a certain specification in terms of protein content.
65. The COT considered that the ED01 was an adequate protection goal, given the potential for increased human exposure to the allergen if it were to be present in food packaging. However, work is still underway with the COT thresholds sub-group to inform FSA decisions on which ED should be used. It was agreed that the choice of benchmark (e.g. ED01) was a risk management decision. Due to the large amount of data required for dose distribution modelling, accurate estimates below ED01 were not feasible.
66. The COT considered that in order to assess whether BBFCMs posed a negligible health risk in practice (if consumption was below the ED01), it would be necessary to understand the effects of processing on the levels of allergens in the final product, and the extent to which they may migrate into food (as is the case for other allergens). The main concern of the COT is contaminating proteins, and the species from which chitin and chitosan is derived.
Next steps
67. At present, no measurements of the amount of allergenic protein in BBFCMs have been identified in the scientific literature. Furthermore, no public usage or consumption data for chitin or chitosan based BBFCMs were identified in the literature or the National Diet and Nutrition Survey (NDNS) database. When such information becomes available, it could be used to provide an indication or estimation of users’ exposures to any allergenic proteins in chitin or chitosan-based BBFCMs.
68. Following a full assessment (which is pending additional data and an FSA/FSS risk management decision on a threshold level for crustacea), a statement on chitosan in bio-based food contact materials will be produced.
69. Regarding any recommendations for future research, the COT agreed that research on the protein content (quantification and characterisation) at different stages of production of BBFCMs (including the final product), and possible migration into packaged food is needed.
COT position paper
January 2024
List of Abbreviations
|
ADI |
acceptable daily intake |
|
BBFCM |
bio-based food contact material |
|
Bw |
bodyweight |
|
COS |
chitooligosaccharide |
|
COT |
Committee on Toxicity of Chemicals in Food, Consumer Products and the Environment |
|
DBPCFC |
double-blind, placebo-controlled food challenge |
|
dm2 |
square decimeter |
|
ED |
eliciting dose |
|
EFSA |
European Food Safety Authority |
|
ELISA |
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
|
EU |
European Union |
|
FAO |
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations |
|
FCM |
food contact material |
|
FSA |
Food Standards Agency |
|
FSANZ |
Food Standards Australia New Zealand |
|
FSS |
Food Standards Scotland |
|
GRAS |
generally recognised as safe |
|
GWP |
global warming potential |
|
IgE |
immunoglobulin E |
|
ISO |
International Organization for Standardization |
|
KDa |
kilodaltons |
|
KFDA |
Korean Food and Drug Administration |
|
LCA |
life-cycle assessment |
|
NAC |
National Aspergillosis Centre |
|
NDNS |
national diet and nutrition survey |
|
NF |
novel food |
|
OML |
overall migration limit |
|
pI |
isoelectric point |
|
PEF |
product environmental footprint |
|
PLA |
poly(lactic) acid |
|
PM |
particulate matter |
|
Ppb |
parts per billion |
|
RfD |
reference dose |
|
SML |
specific migration limit |
|
SPT |
skin prick test |
|
US EPA |
United States Environmental Protection Agency |
|
US FDA |
United States Food and Drug Administration |
|
VOC |
volatile organic compounds |
|
WHO |
World Health Organization |
References
Barennes H., Phimmasane M., & Rajaonarivo C. (2015) Insect consumption to address undernutrition, a national survey on the prevalence of insect consumption among adults and vendors in Laos. PLoS ONE 10(8): e0136458.
Bradley E.L. (2010). FSA Project A03070: Biobased materials used in food contact applications: an assessment of the migration potential: Research report: Biobased materials used in food contact applications: an assessment of the migration potential.
Broekman H.C., Knulst A.C., den Hartog Jager S., et al. (2015) Effect of thermal processing on mealworm allergenicity. Molecular Nutrition and Food Research 59: 1855-1864.
Broekman H., Verhoeckx K.C., den Hartog Jager C.F., et al. (2016) Majority of shrimp-allergic patients are allergic to mealworm. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 137: 1261-1263.
Broekman H.C., Knulst A.C., den Hartog Jager C.F., et al. (2017) Primary respiratory and food allergy to mealworm. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 140: 600-603.
Bueter C.L., Lee C.K., Rathinam V.A., et al. (2011) Chitosan but not chitin activates the inflammasome by a mechanism dependent upon phagocytosis. J Biol Chem 286: 35447-35455.
Boot R.G., Blommaart E.F., Swart E., et al. (2001). Identification of a novel acid mammalian chitinase distinct from chitotriosidase. Journal of Biological Chemistry 276: 6770-6778.
Campos C.A., Gerschenson L.N., & Flores S.K. (2011). Development of Edible Films and Coatings with Antimicrobial Activity. Food Bioprocess Technol. 4: 849-875.
Chae S.Y., Jang M.K., & Nah J.W. (2005) Influence of molecular weight on oral absorption of water soluble chitosans. J Control Release. 102(2): 383-394.
Cleenewerck M.B., Martin P., & Laurent D. (1994). Allergic contact dermatitis due to a moisturizing body cream with chitin. Contact Dermatitis 31(3): 196-197.
Conrado B., Lerodiakonou D., Gowland M.H., et al. (2021) Food anaphylaxis in the United Kingdom: analysis of national data, 1998-2018. BMJ 372: 251.
Daul C.B., Slattery M., Reese G., et al. (1994) Identification of the major brown shrimp (Penaeus aztecus) allergen as the muscle protein tropomyosin. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 105: 49-55.
Deters A., Petereit F., Schmidgall J., et al., (2008) N-acetyl-d-glucosamineoligosaccharides induce mucin secretion from colonic tissue and inducedifferentiation of human keratinocytes, J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 60: 197-204.
Du W.L., Niu S.S., Xu Y.L., et al. (2009) Antibacterial activity of chitosan tripolyphosphate nanoparticles loaded with various metal ions. Carbohydr Polym. 75(3): 385-389.
EFSA (2010) Scientific Opinion on the safety of ‘Chitin-glucan’ as a Novel Food ingredient. EFSA Journal 8(7): 1687: Scientific Opinion on the safety of ‘Chitin‐glucan’ as a Novel Food ingredient - - 2010 - EFSA Journal - Wiley Online Library.
EFSA (2011) Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to chitosan and reduction in body weight (ID 679, 1499), maintenance of normal blood LDL-cholesterol concentrations (ID 4663), reduction of intestinal transit time (ID 4664) and reduction of inflammation (ID 1985) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/20061 EFSA Journal 9(6): 2214: Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to chitosan and reduction in body weight (ID 679, 1499), maintenance of normal blood LDL-cholesterol concentrations (ID 4663), reduction of intestinal transit time (ID 4664) and reduction of inflammation (ID 1985) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006 | EFSA (europa.eu).
EFSA (2014) Scientific Opinion on the evaluation of allergenic foods and food ingredients for labelling purposes. EFSA Journal 12(11): 3894: Scientific Opinion on the evaluation of allergenic foods and food ingredients for labelling purposes | EFSA (europa.eu).
EFSA (2020) Safety of dried yellow mealworm (Tenebrio molitor larva) as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA Journal 19(1): 6343: Safety of dried yellow mealworm (Tenebrio molitor larva) as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 | EFSA (europa.eu).
Fabec B., Hellstrom T., Henrysdotter G., et al. (2000). Active and intelligent food Packaging. A Nordic report on the legislative aspects. Nordic co-operation, p.29: Active and Intelligent Food Packaging: A Nordic Report on the Legislative ... - Google Books.
Fajardo P., Martins J.T., Fuciños C., et al. (2010) Evaluation of a chitosan-based edible film as carrier of natamycin to improve the storability of Saloio cheese. J. Food Eng. 101: 349-356.
FAO/ WHO (2023) Risk assessment of food allergens – Part 2: Review and establish threshold levels in foods for the priority allergens. Meeting Report. Food Safety and Quality Series No. 15. Rome: Risk Assessment of Food Allergens. Part 2: Review and establish threshold levels in foods for the priority allergens (fao.org).
Ferreira A.R., Alves V.D., & Coelhoso I.M. (2016) Polysaccharide-based membranes in food packaging applications. Membranes (Basel) 6:2.
FSANZ (2012) Supporting Document 1: Risk and Technical Assessment Report – Application A1077 Fungal Chitosan as a Processing Aid: A1077-ChitosanAppR-SD1.pdf (foodstandards.gov.au).
Gades M.D. & Stern J.S. (2003) Chitosan supplementation and fecal fat excretion in men. Obes Res. 11(5): 683-688.
Gades M.D. & Stern J.S. (2005) Chitosan supplementation and fat absorption in men and women. J Am Diet Assoc. 105(1): 72-77.
Ghosh T. & Katiyar V. (2020). Ch. 16 Life Cycle Assessment of Chitosan. In book: Advances in Sustainable Polymers. Springer. Eds: Katiyar V., Kumar A., Mulchandani N. (pp.380-381).
Garino C., Mielke H., Knüppel S., et al. (2020) Quantitative allergenicity risk assessment of food products containing yellow mealworm (Tenebrio molitor). Food and Chemical Toxicology 142: 111460.
Han W., Yu Y., Li J., et al. (2011). Application and safety assessment for nano-composite materials in food packaging. Chinese Science Bulletin 56(12): 1216-1225.
Hoff M., Trüeb R.M., Ballmer-Weber B.K., et al. (2003) Immediate-type hypersensitivity reaction to ingestion of mycoprotein (Quorn) in a patient allergic to molds caused by acidic ribosomal protein P2. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 111(5): 1106-10.
Houben G.F., Baumert J.L., Blom W.M., et al. (2020) Full range of population eliciting dose values for 14 priority allergenic foods and recommendations for use in risk characterization. Food and Chemical Toxicology 146: 111831.
Huang B., Xiao D., Tan B., et al., (2016) Chitosanoligosaccharide reduces intestinal inflammation that involvescalcium-Sensing receptor (CaSR) activation in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-challenged piglets. J. Agric. Food Chem. 64: 245-252.
Ifuku S. & H. Saimoto (2012) Chitin nanofibers: preparations, modifications, and applications. Nanoscale 4(11): 3308-18. JFCRF (2011) Japan Food Chemical Research Foundation. List of Existing Food Additives: The Japan Food Chemical Research Foundation (ffcr.or.jp).
Jeevahan J. & Chandrasekaran M. (2019) Nanoedible films for food packaging: a review. J. Mater. Sci. 54: 12290-12318.
Kato Y., Yagami A., & Matsunaga K. (2005) A case of anaphylaxis caused by the health food chitosan. Arerugi 54: 1427-1429.
Kim D., Beck B.R., Heo S.B., et al. (2013) Lactococcuslactis BFE920 activates the innate immune system of olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus), resulting in protection against Streptococcus iniae infection and enhancing feed efficiency and weight gain in large-scale field studies. Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 35: 1585-1590.
Kim K.M., Son J.H., Kim S.K., et al. (2006). Properties of chitosan films as a function of pH and solvent type. Journal of Food Science 71(3): E119-E124.
Konovalova M.V., Markov P.A., Durnev E.A., et al. (2017) Preparation and biocompatibility evaluation of pectin and chitosan cryogels for biomedical application. J Biomed Mater Res. 105(2): 547-556.
Lodhi G., Kim Y-S., Hwang J-W., et al. (2014) Chitooligosaccharide and Its Derivatives: Preparation and Biological Applications. BioMed Research International Article ID 654913.
Lopata A.L., O’Hehir R.E., & Lehrer S.B. (2010) Shellfish allergy. Clinical & Experimental Allergy 40: 850-858.
Madhumathi K., Shalumon K.T., Rani V.V., et al. (2009) Wet chemical synthesis of chitosan hydrogel-hydroxyapatite composite membranes for tissue engineering applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 45(1): 12-15.
Moraru C., Mincea M.M., Frandes M., et al. (2018) A Meta-Analysis on Randomised Controlled Clinical Trials Evaluating the Effect of the Dietary Supplement Chitosan on Weight Loss, Lipid Parameters and Blood Pressure. Medicina 54: 109.
Nguyen M.X.H. (2012) Characterization of allergenic and antimicrobial properties of chitin and chitosan and formulation of chitosan-based edible film for instant food casing. Melbourne, Australia: Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology (RMIT) University, PhD thesis: core.ac.uk/download/pdf/15625643.pdf.
NTP (2017) Technical Report on the Toxicity Study of Chitosan (CASRN 9012-76-4) Administered in Feed to Sprague Dawley [Crl:CD(SD)] Rats. Toxicity Report 93, National Toxicology Program, Public Health Service, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
Ouattara B., Simard R.E., Piette G., et al. (2000) Inhibition of surface spoilage bacteria in processed meats by application of antimicrobial films prepared with chitosan. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 62: 139-148.
Pereira F., Pereira C., & Lacerda M.H. (1998). Contact dermatitis due to a cream containing chitin and a Carbitol. Contact Dermatitis 38(5): 290-291.
Pereira B., Venter C., Grundy J., et al. (2005) Prevalence of sensitization to food allergens, reported adverse reaction to foods, food avoidance, and food hypersensitivity among teenagers. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 116: 884-892.
Qin C., Li H., Liu Y., et al. (2006) Water-solubility of chitosan and its antimicrobial activity. Carbohydrate Polymers 63: 367-374.
Qin Y., Zhang S., Yu J., et al. (2016) Effects of chitin nano-whiskers on the antibacterial and physicochemical properties of maize starch films. Carbohydrate Polymers 147: 372-378.
Reese G., Ayuso R., & Lehrer S.B. (1999) Tropomyosin: An Invertebrate Pan-Allergen. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology 119(4): 247-258.
Remington B.C., Westerhout J., Meima M.Y., et al. (2020) Updated population minimal eliciting dose distributions for use in risk assessment of 14 priority food allergens. Food and Chemical Toxicology 139: 111259.
Romano P., Fabritius H., & Raabe D. (2007). The exoskeleton of the lobster Homarus americanus as an example of a smart anisotropic biological material. Acta Biomaterialia 3(3): 301-309.
Sánchez B., González-Tejedo C., Ruas-Madiedo P., et al. (2011) Lactobacillus plantarum extracellular chitin-binding protein and its role in the interaction between chitin, Caco-2 cells, and mucin. Appl. Environ.Microbiol. 77(3): 1123-6.
Singla A.K. & Chawla M. (2001) Chitosan: some pharmaceutical and biological aspects – an update. J Pharm Pharmacol 53: 1047-1067.
Sinha S., Tripathi P., & Chand S. (2012). A new bifunctional chitosanase enzyme from Streptomyces sp. and its application in production of antioxidant chitooligosaccharides. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology 167: 1029-1039.
Tapola N.S., Lyyra M.L., Kolehmainen R.M. et al. (2008) Safety aspects and cholesterol-lowering efficacy of chitosan tablets. J Am Coll Nutr. 27(1): 22-30.
Taylor G. & Wang N. (2018) Entomophagy and allergies: a study of the prevalence of entomophagy and related allergies in a population living in North-Eastern Thailand. Bioscience Horizons 11(8).
Tee R.D., Gordon D.J., Welch J.A., et al. (1993) Investigation of possible adverse allergic reactions to mycoprotein (‘Quorn’). Clin Exp Allergy 23: 257-60.
Tharanathan R.N. (2003). Biodegradable films and composite coatings: Past, present and future. Trends in Food Science and Technology 14(3): 71-78.
TNO (Netherlands Organisation for Applied Scientific Research) (2009). Repeated-dose (13-week) oral toxicity study in rats with chitin-glucan. Study Report provided to EFSA by Kitozyme.
Todorov S.D., Leblanc J.G., Franco B., et al., (2012) Evaluation of the probioticpotential and effect of encapsulation on survival for Lactobacillus plantarum ST16 Pa isolated from papaya. World J. Microbiol Biotechnol 28: 973-984.
US FDA (2008) HemCon Notification: K080818.pdf (fda.gov).
US FDA (2012) Nutrition Center for Food Safety Applied. GRAS Notice Inventory - Agency Response Letter GRAS Notice No. GRN 000443: GRAS Notice 000443: Shrimp-derived chitosan (archive-it.org) (accessed 01/08/2022).
Van den Broek L.A.M., Knoop R.J.I, Kappen F.H.J., et al. (2015) Chitosan films and blends for packaging material. Carbohydrate Polymers 116: 237-242.
Vasile C. (2018) Polymeric Nanocomposites and Nanocoatings for Food Packaging: A Review. Materials 11: 1834.
Waibel K.H., Haney B., Moore M., et al. (2011) Safety of chitosan bandages in shellfish allergic patients. Military Medicine 176: 1153-6.
Woo C.K. & Bahna S.L. (2011) Not all shellfish “allergy” is allergy! Clinical and Translational Allergy 1: 3.
Yadav M., Goswami P., Paritosh K., et al. (2019) Seafood waste: a source for preparation of commercially employable chitin/chitosan materials. Bioresources and Bioprocessing 6: 8.
Yin M., Lin X., Ren T., et al. (2018) Cytocompatible quaternized carboxymethyl chitosan/poly(vinyl alcohol) blend film loaded copper for antibacterial application. Int J Biol Macromol 120: 992-998.
Zeng J.B., He Y.S., Li S.L., et al. (2012) Chitin whiskers: an overview. Biomacromolecules 13(1): 1-11.